# 除了JDK PROXY、CGLIB,还有3种类代理方式
第3、4、5章暂未使用过,仅做参考
定义接口
public interface IUserApi {
String queryUserInfo();
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
实现接口
public class UserApi implements IUserApi {
public String queryUserInfo() {
return "NULL - 抄袭xfg手册并添加学习过程中的理解与笔记";
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 0. 补充一点反射的知识
@Test
public void test_reflect() throws Exception {
Class<UserApi> clazz = UserApi.class;
Method queryUserInfo = clazz.getMethod("queryUserInfo");
Object invoke = queryUserInfo.invoke(clazz.newInstance());
System.out.println(invoke);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 1. JDK代理方式
//例子 1
public class JDKProxy {
public static <T> T getProxy(Class clazz) throws Exception {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, new Class[]{clazz}, new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(method.getName() + " 你被代理了,By JDKProxy!");
return "NULL - 抄袭xfg手册并添加学习过程中的理解与笔记";
}
});
}
}
@Test
public void test_JDKProxy() throws Exception {
IUserApi userApi = JDKProxy.getProxy(IUserApi.class);
String invoke = userApi.queryUserInfo();
logger.info("测试结果:{}", invoke);
}
/**
* 测试结果:
*
* queryUserInfo 你被代理了,By JDKProxy!
* 19:55:47.319 [main] INFO org.itstack.interview.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:NULL - 抄袭xfg手册并添加学习过程中的理解与笔记
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
//例子 2 该例子是代理 (接口)
interface UserApi{
String getUser();
String updateUser();
}
//这个代理类不用实现要代理的接口,只需要实现JDK的InvocationHandler
class UserApiImpl implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public String invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(method.getName() + " 我已经被JDK Proxy代理了!");
return "NULL";
}
}
@Test
void testJDKProxy() {
UserApi userApi = (UserApi) Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{UserApi.class}, new UserApiImpl());
System.out.println(userApi.getUser());
System.out.println(userApi.updateUser());
}
/*
测试结果:
getUser 我已经被JDK Proxy代理了!
NULL
updateUser 我已经被JDK Proxy代理了!
NULL
*/
// 例子 3 该例子是用于代理 (类class)
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RejectedExecutionProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//要增强的类
private RejectedExecutionHandler target;
//这个是用于业务逻辑的,看业务添加
private SupportThreadPoolExecutor executor;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 执行拒绝策略前自增拒绝次数 & 发起报警等业务逻辑
executor.incrementRejectCount();
System.out.println("线程池触发了任务拒绝...");
//执行完增强功能后,再调用被代理类原来的方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
}
// 自定义线程池 目的是增强线程池功能之统计拒绝策略
public class SupportThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
/**
* 拒绝策略次数统计
*/
private final AtomicInteger rejectCount = new AtomicInteger();
//这个构造函数是带了拒绝策略的,会增强传入的拒绝策略
public SupportThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
//调用父类构造函数构造线程池
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
//代理传入的拒绝策略增强功能
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionProxyInvocationHandler = (RejectedExecutionHandler) Proxy.newProxyInstance(handler.getClass().getClassLoader(),
handler.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new RejectedExecutionProxyInvocationHandler(handler, this));
//使用增强后的拒绝策略代理
setRejectedExecutionHandler( rejectedExecutionProxyInvocationHandler);
}
public SupportThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
/**
* 设置 {@link SupportThreadPoolExecutor#rejectCount} 自增
*/
public void incrementRejectCount() {
rejectCount.incrementAndGet();
}
/**
* 获取拒绝次数
*
* @return
*/
public int getRejectCount() {
return rejectCount.get();
}
}
public class TestDynamicProxy {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 删除 SupportThreadPoolExecutor 构造方法中的拒绝策略
SupportThreadPoolExecutor executor = new SupportThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
1,
1024,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue(1)
);
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy abortPolicy = new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy();
// 创建拒绝策略代理类 代理ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
// 传参:被代理类类加载器、被代理类实现的接口、代理实现类
//newProxyInstance方法用来返回一个代理对象,这个方法总共有3个参数,ClassLoader loader用来指明生成代理对象使用哪个类装载器,
// Class<?>[] interfaces用来指明生成哪个对象的代理对象,通过接口指定,InvocationHandler h用来指明产生的这个代理对象要做什么事情。
// 所以我们只需要调用newProxyInstance方法就可以得到某一个对象的代理对象了。
RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler = (RejectedExecutionHandler) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
abortPolicy.getClass().getClassLoader(),
abortPolicy.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new RejectedExecutionProxyInvocationHandler(abortPolicy, executor)
);
// 线程池 set 拒绝策略代理类
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(rejectedExecutionHandler);
// 测试流程
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
// 无限睡眠, 以此触发拒绝策略.(此处有异常, 为了减少无用代码, 省略...)
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
// ignore
}
}
Thread.sleep(50);
System.out.println(String.format("线程池拒绝策略次数 :: %d", executor.getRejectCount()));
}
/**
* 日志打印:
*
* 线程池触发了任务拒绝...
* 线程池拒绝策略次数 :: 1
*/
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
- 指数:⭐⭐
- 场景:中间件开发、设计模式中代理模式和装饰器模式应用
- 点评:这种JDK自带的类代理方式是非常常用的一种,也是非常简单的一种。基本会在一些中间件代码里看到例如:数据库路由组件、Redis组件等,同时我们也可以使用这样的方式应用到设计模式中。
- 注意:该接口的所有方法都会被代理
- 例子1 这里使用了匿名内部类而没有使用实现类,通过代理的方式进行的操作。
- 例子2 相对于例子1 也可以自行新建一个类实现InvocationHandler。
- 例子3 相对于前两个例子,这个例子是比较进阶且代理了class而不是interface
有接口实现的创建方式和无接口实现的创建方式,所产生的动态代理类有什么区别?
- 有接口实现是对 InvocationHandler#invoke 方法调用,invoke 方法通过反射调用被代理对象 RejectedExecutionHandler#rejectedExecution
- 无接口实现则是仅对 InvocationHandler#invoke 产生调用。所以,有接口实现返回的是被代理对象接口返回值,而无实现接口返回的仅是 invoke 方法返回值。
- 个人理解这段话:无接口实现就是例子1、2,这两个例子只会调用InvocationHandler#invoke方法,返回值由invoke方法决定。
而例子3可以调用InvocationHandler#invoke后自行在InvocationHandler#invoke方法中再调用被代理类的方法,返回值由被代理类决定。
# 2. CGLIB代理方式
class CglibProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object newInstall(Object object) {
return Enhancer.create(object.getClass(), this);
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我被cglib proxy代理了!");
return proxy.invokeSuper(obj,args);
}
}
static class UserApiImpl implements UserApi{
@Override
public String getUser() {
return "NULL";
}
@Override
public String updateUser() {
return "NULL";
}
}
@Test
void testCglibProxy(){
CglibProxy cglibProxy = new CglibProxy();
UserApi userApi = (UserApi) cglibProxy.newInstall(new UserApiImpl());
String invoke = userApi.getUser();
log.info("测试结果:{}", invoke);
String invoke1 = userApi.updateUser();
log.info("测试结果:{}", invoke1);
}
/**
* 测试结果:
*
* 我被cglib proxy代理了!
* 测试结果:NULL
* 我被cglib proxy代理了!
* 测试结果:NULL
*
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
//例子2
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.example.demo.service.AliPayService;
import org.example.demo.service.PayService;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class PayServiceCGLIBInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
//被代理对象
private Object target;
public PayServiceCGLIBInterceptor(Object target){
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
//1.安全检查
System.out.println("安全检查");
//2.记录日志
System.out.println("记录日志");
//3.时间统计开始
System.out.println("记录开始时间");
//通过cglib的代理方法调用
Object retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, args);
//4.时间统计结束
System.out.println("记录结束时间");
return retVal;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//被代理类
PayService target= new AliPayService();
//跟JDK proxy 例子3相似
PayService proxy= (PayService) Enhancer.create(target.getClass(),new PayServiceCGLIBInterceptor(target));
proxy.pay();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
- 指数:⭐⭐⭐
- 场景:Spring、AOP切面、鉴权服务、中间件开发、RPC框架等
- 点评:CGLIB不同于JDK,它的底层使用ASM字节码框架在类中修改指令码实现代理,所以这种代理方式也就不需要像JDK那样需要接口才能代理。同时得益于字节码框架的使用,所以这种代理方式也会比使用JDK代理的方式快1.5~2.0倍。 但是在 JDK 8 以上的版本中,因为 JDK 动态代理做了专门的优化,所以它的性能要比 CGLIB 高。
- 简单来说,JDK 动态代理要求被代理类实现接口,而 CGLIB 要求被代理类不能是 final 修饰的最终类。
- 同样的,被代理类的所有方法都会被增强
# 3. ASM代理方式
public class ASMProxy extends ClassLoader {
public static <T> T getProxy(Class clazz) throws Exception {
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader(clazz.getName());
ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter(classReader, ClassWriter.COMPUTE_MAXS);
classReader.accept(new ClassVisitor(ASM5, classWriter) {
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, final String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
// 方法过滤
if (!"queryUserInfo".equals(name))
return super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
final MethodVisitor methodVisitor = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
return new AdviceAdapter(ASM5, methodVisitor, access, name, descriptor) {
@Override
protected void onMethodEnter() {
// 执行指令;获取静态属性
methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
// 加载常量 load constant
methodVisitor.visitLdcInsn(name + " 你被代理了,By ASM!");
// 调用方法
methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);
super.onMethodEnter();
}
};
}
}, ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES);
byte[] bytes = classWriter.toByteArray();
return (T) new ASMProxy().defineClass(clazz.getName(), bytes, 0, bytes.length).newInstance();
}
}
@Test
public void test_ASMProxy() throws Exception {
IUserApi userApi = ASMProxy.getProxy(UserApi.class);
String invoke = userApi.queryUserInfo();
logger.info("测试结果:{}", invoke);
}
/**
* 测试结果:
*
* queryUserInfo 你被代理了,By ASM!
* 20:12:26.791 [main] INFO org.itstack.interview.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:小傅哥,公众号:bugstack虫洞栈 | 沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
- 指数:⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 场景:全链路监控、破解工具包、CGLIB、Spring获取类元数据等
- 点评:这种代理就是使用字节码编程的方式进行处理,它的实现方式相对复杂,而且需要了解Java虚拟机规范相关的知识。因为你的每一步代理操作,都是在操作字节码指令,例如:Opcodes.GETSTATIC、Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL,除了这些还有小200个常用的指令。但这种最接近底层的方式,也是最快的方式。所以在一些使用字节码插装的全链路监控中,会非常常见。
- 这种方法比较高级,没办法做出自己备注 TODO:待更新
# 4. Byte-Buddy代理方式
public class ByteBuddyProxy {
public static <T> T getProxy(Class clazz) throws Exception {
DynamicType.Unloaded<?> dynamicType = new ByteBuddy()
.subclass(clazz)
.method(ElementMatchers.<MethodDescription>named("queryUserInfo"))
.intercept(MethodDelegation.to(InvocationHandler.class))
.make();
return (T) dynamicType.load(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()).getLoaded().newInstance();
}
}
@RuntimeType
public static Object intercept(@Origin Method method, @AllArguments Object[] args, @SuperCall Callable<?> callable) throws Exception {
System.out.println(method.getName() + " 你被代理了,By Byte-Buddy!");
return callable.call();
}
@Test
public void test_ByteBuddyProxy() throws Exception {
IUserApi userApi = ByteBuddyProxy.getProxy(UserApi.class);
String invoke = userApi.queryUserInfo();
logger.info("测试结果:{}", invoke);
}
/**
* 测试结果:
*
* queryUserInfo 你被代理了,By Byte-Buddy!
* 20:19:44.498 [main] INFO org.itstack.interview.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:小傅哥,公众号:bugstack虫洞栈 | 沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
- 指数:⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 场景:AOP切面、类代理、组件、监控、日志
- 点评:Byte Buddy 也是一个字节码操作的类库,但 Byte Buddy 的使用方式更加简单。无需理解字节码指令,即可使用简单的 API 就能很容易操作字节码,控制类和方法。比起JDK动态代理、cglib,Byte Buddy在性能上具有一定的优势。另外,2015年10月,Byte Buddy被 Oracle 授予了 Duke's Choice大奖。该奖项对Byte Buddy的“ Java技术方面的巨大创新 ”表示赞赏。
- 这种方法比较高级,没办法做出自己备注 TODO:待更新
# 5. Javassist代理方式
public class JavassistProxy extends ClassLoader {
public static <T> T getProxy(Class clazz) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 获取类
CtClass ctClass = pool.get(clazz.getName());
// 获取方法
CtMethod ctMethod = ctClass.getDeclaredMethod("queryUserInfo");
// 方法前加强
ctMethod.insertBefore("{System.out.println(\"" + ctMethod.getName() + " 你被代理了,By Javassist\");}");
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
return (T) new JavassistProxy().defineClass(clazz.getName(), bytes, 0, bytes.length).newInstance();
}
}
@Test
public void test_JavassistProxy() throws Exception {
IUserApi userApi = JavassistProxy.getProxy(UserApi.class)
String invoke = userApi.queryUserInfo();
logger.info("测试结果:{}", invoke);
}
/**
* 测试结果:
*
* queryUserInfo 你被代理了,By Javassist
* 20:23:39.139 [main] INFO org.itstack.interview.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:小傅哥,公众号:bugstack虫洞栈 | 沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
- 指数:⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 场景:全链路监控、类代理、AOP
- 点评:Javassist 是一个使用非常广的字节码插装框架,几乎一大部分非入侵的全链路监控都是会选择使用这个框架。因为它不想ASM那样操作字节码导致风险,同时它的功能也非常齐全。另外,这个框架即可使用它所提供的方式直接编写插装代码,也可以使用字节码指令进行控制生成代码,所以综合来看也是一个非常不错的字节码框架。
- 这种方法比较高级,没办法做出自己备注 TODO:待更新
# 总结
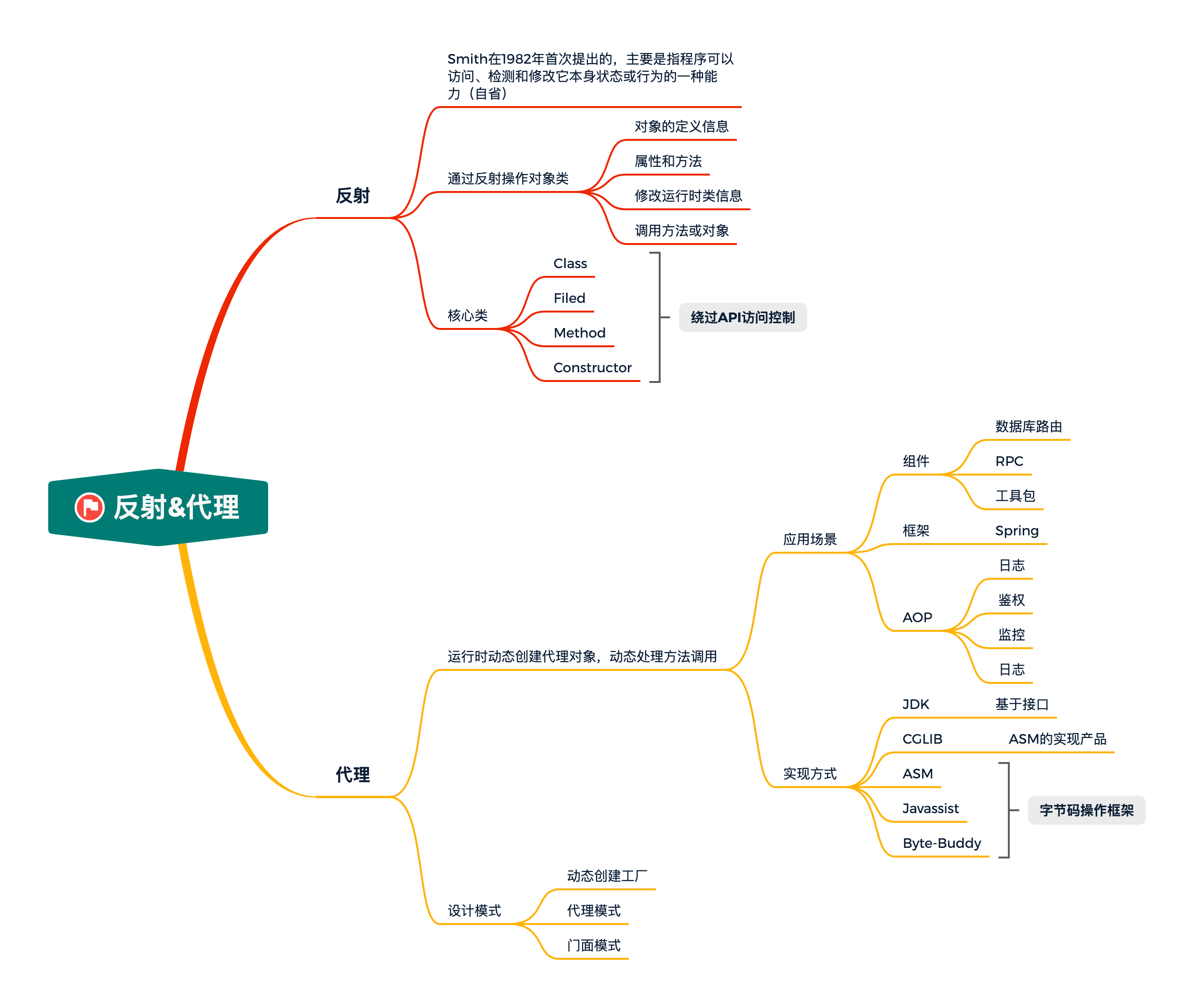
- 代理的实际目的就是通过一些技术手段,替换掉原有的实现类或者给原有的实现类注入新的字节码指令。而这些技术最终都会用到一些框架应用、中间件开发以及类似非入侵的全链路监控中。
- 一个技术栈深度的学习能让你透彻的了解到一些基本的根本原理,通过这样的学习可以解惑掉一些似懂非懂的疑问,也可以通过这样技术的拓展让自己有更好的工作机会和薪资待遇。
- 这些技术学起来并不会很容易,甚至可能还有一些烧脑。但每一段值得深入学习的技术都能帮助你突破一定阶段的技术瓶颈。
← ThreadLocal volatile →